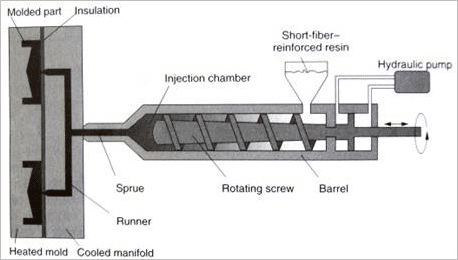
Popular manufacturing process for plastic products and here we explain how product design considerations must be made.
Advantages:
- Allows excellent surface finish, repeatability and speed.
- Mould decorations can be integrated into the actual moulding process, eliminating the need for a separate printing process
- Colouring is possible
- Inserts and snap-fits can be moulded to aid assembly
Disadvantages:
- Tooling costs are very high, depending on the number of cavities and complexity of the design
- Large parts take longer to solidify and thus can increase mould cycle times
Design Considerations:
- High volume production runs only
- Mould cycle times depend on the size of the part
- Warping and shrinkage can occur after the part is ejected from the mould cavity, ribbing can help reduce these effects
- Stress can occur at sharp corners and draft angles
- Draft angles should be at least 0.5o
- The melted plastic must inject into the thickest section and finish at the thinnest
- Wall thickness should be uniform (ideal) or within 10%
- Uneven wall sections cause the part to warp
- Ribs should not exceed 5 times the height of the wall thickness, so use many shallow ribs instead
Source: Manufacturing processes for design professionals; Rob Thompson [2007]